People have been divided into buyers and sellers since the day the idea of trade emerged. Both always seek their own benefit.
Sellers strive to sell their goods at the highest possible price. Buyers want to find the best price among the offers.
This is what trading is all about. No matter how much time passes or how many new trading methods are invented, this principle remains unchanged. The buyer aims for the lowest price, while the seller aims for the highest.
International platforms for trading currencies, stocks, crypto, etc. are no exception.
Exchange trading implies the presence of numerous offers that define the quote of an asset. The range between them can vary greatly. Their calculation becomes the basis for the concept of "stock spread."
In other words, a spread is the foundation of trading, its key indicator.
Stock spread in trading
This term refers to the difference between the most favorable buy price and the sell price in trading. This element is an integral part of all markets that trade futures, stocks, cryptocurrencies, or other instruments.
Most often, the concept of spread is used to describe prices or returns: Therefore, there is the following difference between
- the buy price and the sell price;
- the current value of an instrument and its value after a period of time;
- the prices of the same asset class. For example, the difference between the price of Brent and WTI;
- the returns of equities issued by different entities;
- the yields of bonds with different maturity dates.
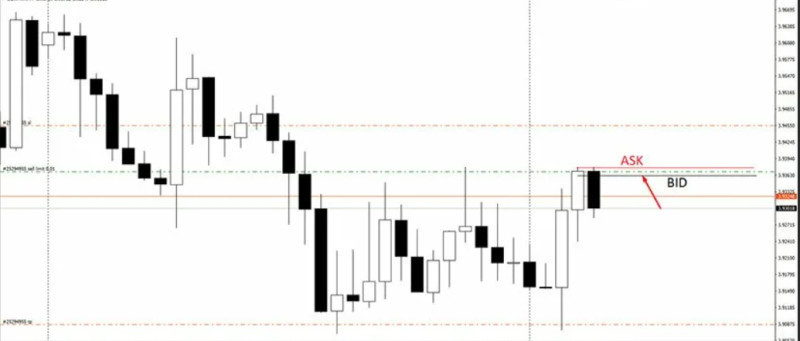
However, the most common type of spread is the difference between the Bid price and the Ask price.
Here is a formula to calculate a spread:
Best buy price - best sell price = spread
To express it as a percentage, a slightly more complex calculation is needed:
Best buy price - best sell price / Best buy price x 100 = spread in %
In addition to the traditional concept, a spread may also include differences in the price of an asset on various trading platforms and the price gap with a correlation.
Types of spread based on size:
- Wide spreads indicate a significant price difference
- Narrow spreads reflect a minimal difference between the buy price and the sell price.
So, what is considered the best spread? The answer to this question is simple on the one hand but requires additional explanation on the other.
Simply put, evaluating the size of spreads can only be done in the context of one asset. It is meaningless to compare the spreads of different instruments.
This is because a small spread for one futures contract or currency pair is the norm but an exception for others. Spreads often have a direct correlation with the price of an asset and several other factors.
| All in all, a spread is a gap between the highest buy price and the lowest sell price of an asset in the market within a preset time period. |
There are two driving forces for a spread. On the one side, there are buyers who want to acquire an asset at the lowest possible price. On the other side, there are sellers who also want to sell the asset at the highest possible price.
The moment when a compromise between these opposing forces is reached marks the conclusion of a trade. Until then, the market shows fluctuations in value.
Spread vs brokerage commission
Brokerage services are services provided by an intermediary to access the market, and they are not free of charge. There are two ways to pay for brokerage services:
1. Stock spread
The broker will receive the difference between the buy price and sell price, or the difference between the Ask price and the Bid price, as compensation.
2. Commissions
It is about a fee charged by the broker, which is usually levied either when opening or closing a position. Sometimes, it may be charged both at the opening and closing of a trade, which is referred to as a double commission.
Important! A commission can be fixed or it can be a preset percentage of a trade.
Different ways of cooperation with brokerage companies have their advantages and disadvantages. Traders often choose payment methods based on their trading strategies.
This allows them to pick the most advantageous option.
For example, long-term investors prefer a fixed commission. Those who are accustomed to conducting many trades throughout the day may opt for a spread or percentage-based payment.
Important! Never trust brokers who offer overly tempting trading conditions such as zero spreads or suspiciously low commissions.
Spread in exchange trading
In exchange trading, spread refers to the difference between two prices. There are several ways to measure it, using monetary units or percentages for example. If trading takes place in the futures market, it is often measured in pips.
An exchange spread is an indicator of the liquidity of a trading instrument. The asset with the lowest spread is considered the most liquid one.
The perfect scenario is when the spread is measured in fractional percentages. Even a small value can sometimes play a crucial role.
Where does a spread come from? It is usually set by market makers.
These are companies that enter into an agreement with exchanges. The task of market makers is to ensure a consistently high level of asset liquidity.
How can an investor find out the size of a spread? It is enough to refer to the order book.
Order book
The order book is a table that reflects all buy orders at a specific price, as well as the corresponding sell orders. In addition, it displays trading volumes.
| The order book is a list of buy and sell orders illustrated as a table with values. |
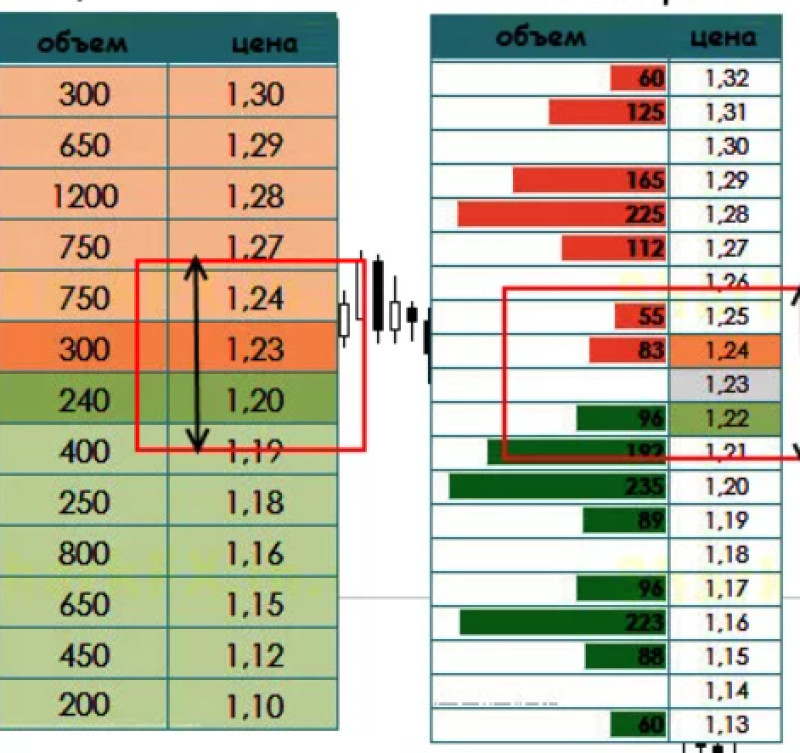
Sell orders are usually listed at the top of the table and are often colored red, or different shades of pink. Sell orders are also referred to as "Ask," meaning "demand."
Buy orders are listed at the bottom of the table and are usually highlighted in various shades of green. Buy orders are referred to as "Bid," meaning "offer."
The closer a bid order is to the middle of the list, the higher the buy price. Conversely, ask orders with the lowest sell price will be positioned toward the middle.
A zone in the middle is neutral. The difference between prices in the order book illustrates a spread. Sometimes, this difference is so small that it amounts to just a few cents.
The order book is the primary tool for identifying spread changes. There are usually three types of orders in the order book.
Types of orders
| Name | Features |
| Market order | Orders to buy or sell an asset immediately, except for cases when there are no counter offers. |
| Limit orders | Orders to buy or sell an asset at a specified price. They will not be executed unless the asset’s price meets those qualifications. Once both parties agree to the terms, the order disappears from the order book. |
| Conditional orders | Orders that will only be executed if certain criteria are met. |
Important! The order book displays only limit orders, as market orders are executed immediately and therefore cannot be shown.
Based on their volume, all orders can be divided into three types:
- Small
- Medium
- Large
Notably, this categorization is highly subjective, as liquidity and the total daily trading volume of an asset play a significant role. These categories can vary, so there is no need to pay too much attention to them.
Limit orders have an expiration period. They expire in a day if they have not been fulfilled.
Earlier orders are executed first.
Highly liquid assets have minimal spreads, and the number of closed orders exceeds a thousand during a single trading day.
Sometimes there is no trading difference at all. This happens when the order book is formed exclusively from Ask or Bid orders. In such a case, it is recommended that you set your price in the order book and wait for a response.
What factors influence the spread? How does the order book work?
Factors shaping the spread size:
1. Liquidity
It is about the popularity and demand for the underlying financial instrument. The more active the trading, the more liquid the asset. As a result, there are more traders involved, and the likelihood of gaps or price slippage decreases significantly.
The difference between the buy and sell prices is smaller in highly liquid markets compared to markets with fewer participants.
For example, the natural gas futures market has a higher spread because it is not widely popular among investors. The same applies to certain currencies such as the Canadian dollar or the Swiss franc.
2. Market conditions
Economic, political, and other factors have a significant impact on the market. Experienced traders know that periods of important news announcements can be highly volatile.
Asset prices undergo great transformations, which leads to an increase in the spread. Investors prefer to avoid such situations and may refrain from trading to avoid losses.
3. Overall trading volume
The number of traders is a highly variable factor. If there are many, the spread will be narrower. Conversely, when the number of traders decreases, the spread tends to increase.
Important! The absence of buyers or sellers can lead to a situation where the spread disappears.
4. Broker affiliate programs
Many affiliate programs developed by brokerage companies are based on providing rewards from the spread. Therefore, expanding the number of partners can lead to an increase in the trading spread, and vice versa.
Thus, the spread is an integral part of exchange trading, and its size is not constant. It changes based on specific factors. Analyzing these factors allows traders to better understand the market situation and execute trades more effectively.
About spread
An exchange spread is a complex component of the trading system that can be challenging to analyze. However, it doesn't mean that you cannot understand its intricacies.
On the contrary, a trader's success is often determined by their knowledge about this concept and their ability to work with it.
To better understand its features, let's take an example such as buying clothing.
If you are an entrepreneur whose primary business involves buying ready-made clothing from one place and selling it elsewhere, you can easily imagine how the exchange difference works.
In order to make a profit from selling clothing, you first need to buy it at a cheaper price and then sell it at a higher price to gain an advantage.
The difference in cost from buying to selling clothing represents a hypothetical exchange spread. The difference in price speculation is referred to as profit or income.
In the context of trading on international markets, brokerage companies, acting as intermediaries between investors who take turns as buyers or sellers, earn an income.
This example perfectly illustrates the key issues. It becomes evident that you will unlikely sell a product at a high price. The same applies to assets: unexecuted orders expire the next day.
Therefore, the benefit of selling at a favorable price becomes evident for the three participants in the exchange market:
- The seller earns an income.
- The buyer spends as little money as possible.
- The broker receives their compensation (spread).
Exchange trading involves several types of spreads.
- Fixed spreads
This type is common in the currency market. Here brokers determine the size of their reward.
Each contract has its own specification, where you can find a spread.
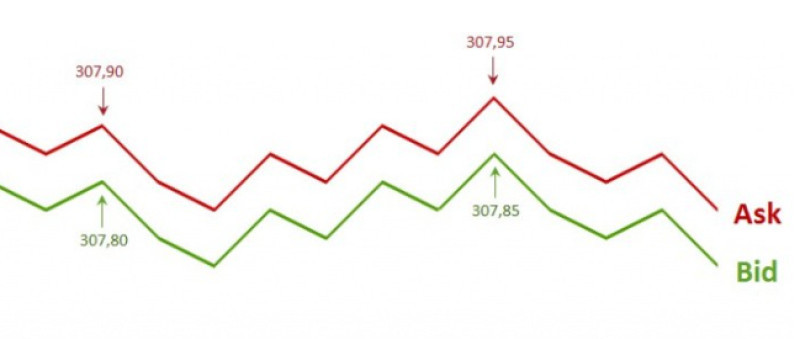
Fixed spreads remain unchanged on Forex regardless of various factors. The size is measured in pips.
2. Floating spreads
These spreads are common for both currency and exchange trading. Their size is determined by market makers.
After signing an agreement with the exchange, market makers commit to maintaining the spread within predetermined limits. Their main task is to prevent the spread from increasing steeply.
In cases where market makers are absent, the spread is determined by market participants.
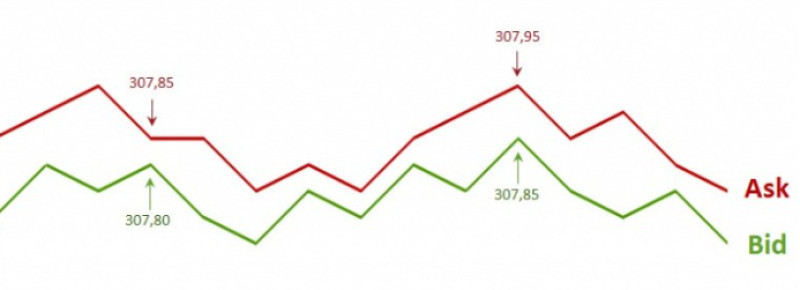
Floating spreads are variable and influenced by the factors described above. In this case, the activity of buyers and sellers is of great importance.
3. Intermarket spreads
This is the price difference between correlated, i.e., interconnected, commodities on different trading platforms.
For example, Yandex shares are traded simultaneously on both the American and Moscow stock exchanges, with prices varying between the two platforms. This difference is referred to as a spread.
Important! Sometimes conducting such trades can be unprofitable due to additional fees. Therefore, you should carefully consider all pros and cons beforehand.
4. Intramarket spreads:
These are spreads between closely correlated commodities within one market.
They are more popular among stock traders. Here it is about shares of the same issuer but of different categories, such as common and preferred stocks.
They are also encountered in futures trading, where the spread is the price difference between contracts at specific time intervals, such as different delivery months.
5. Buy-side spreads
It is formed when a buyer acquires an asset at the best price, i.e., through a market order.
6. Sell-side spreads
It is formed when an asset is sold at the most favorable price, i.e., through a market order.
7. Calendar spreads
This type is specific to futures markets, where trading involves instruments with different order execution dates.
Simply put, a calendar spread is the price difference between the same futures contracts with different delivery dates.
Some traders favor this type of trading and develop entire strategies around it.
Depending on trading volume and buyer interest, all currencies on Forex can be divided into several groups based on price levels.
Three types of currencies based on stock spread difference:
| No. | Type | Feature | Example |
| 1. | Major pairs | Instruments with small spreads in the range between 0 and 5 pips. They are the most popular among investors | EUR/USD |
| 2. | Minor currency pairs | Instruments with medium spreads in the range from 5 to 10 pips | GBP/NZD |
| 3. | Exotic pairs | Instruments with large spreads from 10 pips and above. These are often combinations of a popular currency with an unpopular one in the market. | DKK/PLN |
It is important to remember that spread conditions can vary from broker to broker. Therefore, you should carefully consider the terms of cooperation beforehand.
How do spreads work?
An exchange spread is a crucial element of trading. It plays a decisive role when operating in different markets.
Its size can significantly impact the overall profitability of a trader. In some cases, it can even lead to losses even though it is a potentially profitable trade.
Therefore, it is important to carefully calculate the spread and adhere to a set of rules and recommendations to avoid serious problems.
How to work with spreads:
1. Ignoring the spread in intraday trading is impossible as it is of utmost importance here.
Setting appropriate Stop Loss and Take Profit orders can help reduce its impact so that you can focus on other aspects of trading.
2. In long-term trading, a floating spread is commonly used because smaller values are convenient for opening positions.
As for medium-term trading, the period of lowest volatility plays a crucial role because the spread will be minimal during this time.
3. In the Forex market, the buy price tends to be slightly higher than what is shown on the chart. Therefore, when receiving a signal to close a trade, it is important to add a Take Profit level and the spread to the calculation. This is the only way to get accurate results.
4. The most popular currency pair, EUR/USD, has one of the smallest spreads that can be ignored.
5. When selling, Stop Loss orders may trigger earlier than the price reaches a certain level. There are risks that they may react to the spread when executing the trade.
To avoid this, you should set this order slightly higher. Calculating this value involves adding the spread to the desired level with a few extra pips.
A Take Profit order should be set for below the market price when selling.
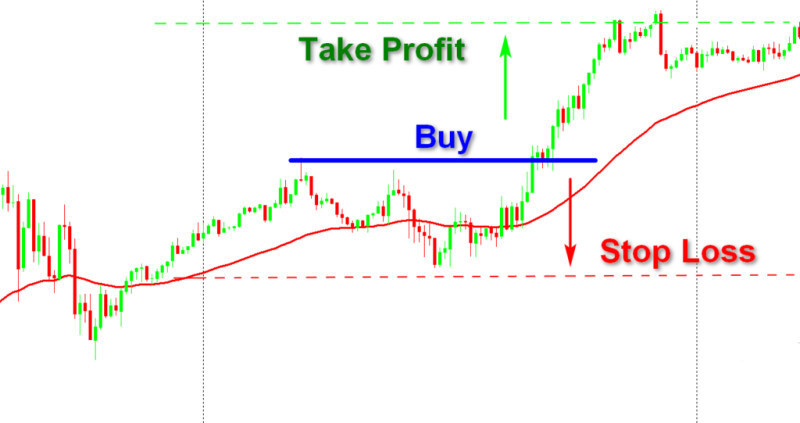
6. Investments in assets with minimal spread and high trading volumes are considered lucrative for the stock market.
7. It is not advisable to purchase assets during a phase of active growth in the spread. Losses in this case are inevitable.
Important! Traders can reduce the size of the spread by placing limit orders. These orders will be executed either at the set price or at a higher one.
However, there is a risk that the order may not be executed at all. This is usually the case during periods of sharp price fluctuations.
Currently, there are numerous programs for analyzing the spread. They help determine the most advantageous entry point.
However, you should never rely solely on these indicators. It is better to use additional tools that confirm the accuracy of signals.
There are programs designed especially for displaying the spread size. All you need is to open the settings menu of your trading platform.
After enabling the corresponding function, the spread size will be displayed in the tick chart table alongside the Ask and Bid prices. However, it does not provide an analysis of the current situation.
Example of what spread is
There is a certain difference between calculating the spread for the forex market and the stock market. Let's provide examples of calculations for each of these markets.
1. Calculating the spread for Forex.
In the forex market, the spread represents the difference between the highest buy price and the lowest sell price, i.e., between the Ask and Bid prices of a currency pair.
The difference between these prices is measured in pips.
A pip is the fourth decimal place in the currency exchange rate.
Let's take USD/CHF as an example for calculating the spread.
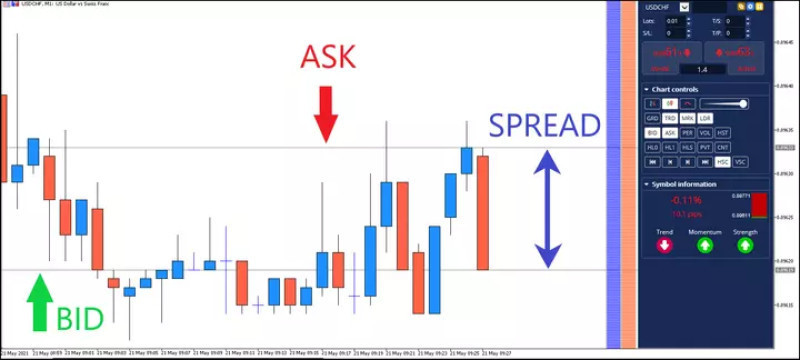
The Ask price here is 0.89633, and the Bid price is 0.89619.
The spread is the difference between Bid and Ask, which can be found by simple subtraction.
0.89633 (Ask) - 0.89619 (Bid) = 0.00014 0.00014 = 14 pips The spread for USDCHF is 14 pips. |
This example illustrates the level of spread over a specific period. Its size changes with time due to volatility and overall trading volumes.
2. Calculating the spread for the stock market
In the stock market, the spread represents the difference between the bid and ask prices of an asset.
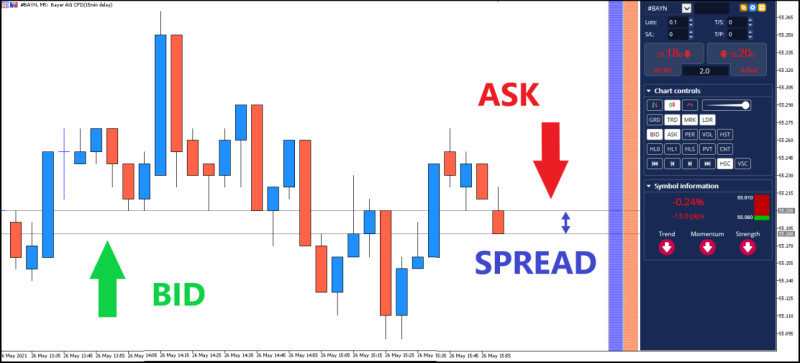
According to the above chart, the Ask price is around €55,200, while the Bid price is €55,180. To determine the trading spread, you need to find the difference between them.
55,200 (Ask) - 55,180 (Bid) = 0.020 €0.020 euros = 2 cents The spread for USD/CHF is 2 cents per share. |
In the stock market, the spread is also a variable value that changes depending on market conditions and other factors.
The most important thing when trading any instrument is to avoid a large spread. This is essential for intraday traders.
However, there is a whole strategy for profiting from the spread, called scalping within the order book.
It is rarely used as it requires preparation and experience. Nevertheless, there are enthusiasts who successfully employ it.
Conclusion
The main goal of trading is to make a profit. Its size depends not only on investors’ experience but also on numerous market-related factors.
One of these factors is the price difference between buying and selling. The market spread is the key parameter that can turn an initially profitable trade into a losing one.
Therefore, it is crucial to be able to navigate the intricacies of spread formation and its impact on different international markets. Additionally, careful selection of a broker is crucial as the spread size also depends on the brokerage company.
However, the most important aspect for any trader remains their skill set, which allows them to build a strategy that generates income regardless of the trading stock spread.
You may also like:
Standard deviation trading strategy








 Back to articles
Back to articles

